Summary
Virtual Reality (VR) is redefining learning by turning abstract concepts into immersive, hands-on experiences. Instead of reading, watching, or listening, learners practice skills in realistic environments that simulate real-world pressure and context. This article explains how VR is transforming education and training, where organizations make costly mistakes, and how to implement VR learning that delivers measurable results.
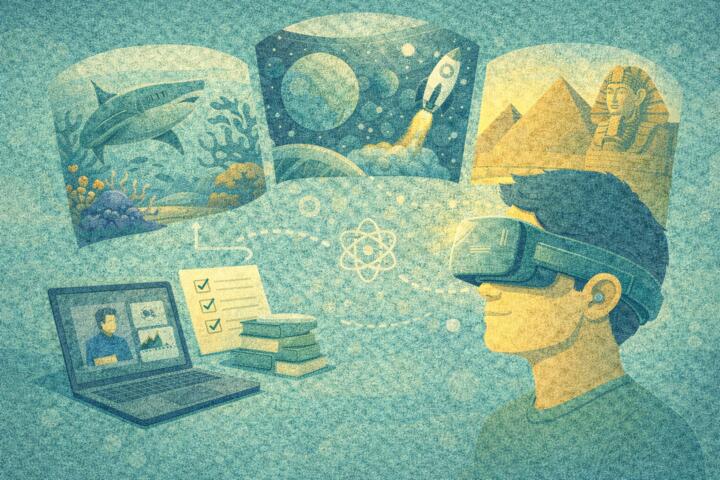

Overview: What VR in Learning Actually Means
Virtual Reality in education is not about headsets or visual effects—it is about experiential learning. VR places learners inside simulated environments where they can practice decisions, actions, and workflows safely.
A well-designed VR learning experience includes:
-
spatial immersion (3D environments),
-
interaction (hands, tools, movement),
-
scenario logic (cause-and-effect),
-
performance feedback.
For example, medical students using VR can practice surgical procedures repeatedly without risking patient safety. According to PwC research, learners trained with VR complete training up to 4× faster than classroom learners and show higher confidence in applying skills.
In corporate environments, VR is increasingly used for safety training, technical skills, and leadership simulations—areas where mistakes in the real world are expensive or dangerous.
Main Pain Points in Traditional Learning Models
1. Passive Knowledge Consumption
Most traditional learning relies on lectures, slides, and videos.
Why this matters:
People remember far more from doing than from listening.
Consequence:
Studies show that lecture-based learning often results in retention rates below 30% after a few weeks.
2. Lack of Real-World Context
Learning content is often detached from real environments.
Real situation:
Employees pass tests but fail in actual work situations because they never practiced under realistic conditions.
3. High Cost of Physical Training
Hands-on training requires:
-
instructors,
-
equipment,
-
travel,
-
downtime.
Impact:
Scaling training becomes slow and expensive.
4. Safety and Risk Constraints
Certain skills cannot be practiced safely in real life.
Examples:
-
emergency response
-
heavy machinery operation
-
hazardous environments
VR-Based Solutions and Practical Recommendations
Use VR for High-Risk, High-Value Skills
What to do:
Apply VR where mistakes are costly or dangerous:
-
medical procedures,
-
safety drills,
-
equipment operation.
Why it works:
Learners can fail safely and repeat scenarios until mastery.
In practice:
Strivr reports that VR-trained employees show 30–40% higher performance confidence compared to traditional training.
Design Scenarios, Not Experiences
What to do:
Focus on realistic scenarios with clear objectives:
-
decision points,
-
consequences,
-
feedback loops.
Why it works:
Learning transfers better when context matches reality.
Tools and platforms:
-
Unity
-
Unreal Engine
-
Pixo VR
Integrate VR With Learning Analytics
What to do:
Track:
-
reaction time,
-
error frequency,
-
decision paths,
-
completion metrics.
Why it works:
VR generates behavioral data, not just test scores.
Results:
Organizations using VR analytics improve skill mastery rates by 20–35%.
Combine VR With Other Learning Formats
What to do:
Use VR as part of blended learning:
-
pre-VR theory modules,
-
VR practice,
-
post-session reflection.
Why it works:
VR reinforces, not replaces, foundational knowledge.
Mini Case Examples
Case 1: Corporate Safety Training
Company: Walmart
Problem: Inconsistent safety training across stores
Solution:
VR simulations for compliance and safety scenarios
Result:
-
Training completion time reduced
-
Higher retention and fewer safety incidents
Case 2: Medical Education
Organization: Mayo Clinic
Problem: Limited access to real surgical practice
Solution:
VR-based procedural training
Result:
-
Faster skill acquisition
-
Reduced training costs
-
Improved learner confidence
VR Learning vs. Traditional Training Comparison
| Dimension | Traditional Learning | VR-Based Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Engagement | Low to moderate | High |
| Risk | Real-world consequences | Safe simulation |
| Scalability | Limited | High |
| Feedback | Delayed | Real-time |
| Skill transfer | Inconsistent | Strong |
Common Mistakes (and How to Avoid Them)
Mistake: Using VR for simple knowledge delivery
Fix: Reserve VR for experiential skills
Mistake: Prioritizing visuals over learning goals
Fix: Design around objectives and outcomes
Mistake: Ignoring motion comfort
Fix: Follow VR ergonomics and usability standards
Author’s Insight
I’ve seen VR training succeed where traditional methods failed—especially in high-risk and high-pressure environments. The biggest mistake organizations make is treating VR as a novelty instead of a learning system. When VR scenarios are aligned with real tasks and measured properly, learning outcomes improve dramatically. Start small, focus on one skill, and scale based on results.
Conclusion
Virtual Reality is transforming learning by making practice safe, scalable, and deeply engaging. Its real value lies in experiential design, analytics, and integration with broader learning ecosystems. Organizations that use VR strategically—not superficially—build stronger skills, reduce risk, and accelerate learning.